The main difference between SEO vs SEM
The main distinction between SEO and SEM lies in their approaches to improving your website’s visibility in search results. SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, focuses on enhancing your web pages to rank higher organically, without any cost, while SEM, or Search Engine Marketing, employs paid advertising to secure top positions in the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
SEO involves optimizing both the visible elements of your web pages and the underlying technical aspects to boost their organic rankings. It emphasizes long-term growth in organic traffic and search engine positioning.
On the other hand, SEM encompasses paid advertising tactics like pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, where advertisers bid on keywords to ensure their ads appear prominently in SERPs, leading to immediate visibility and traffic.
PPC advertising is particularly effective because you only incur costs when someone clicks on your ad and visits your website. For instance, on Google, you can set a daily budget as low as £1, making it a cost-effective advertising option for many small businesses. Additionally, you can tailor your ads to specific locations and demographics, such as age groups and income levels.
While SEO demands ongoing effort and patience to see results, SEM provides quick visibility but requires continuous investment to sustain traffic. Both strategies are crucial components of digital marketing, and understanding their differences can guide you in selecting the best approach to connect with your target audience. The benefits of your SEO efforts will persist over time, whereas SEM will only be effective as long as you continue to fund and run the ads.
When to use SEO only:
Use SEO only when you are trying to rank for a keyword or phrase which doesn’t have a lot of big websites also competing for the same topic, and hence you have a much better chance of appearing high up in the search results. In this case, SEO alone should yield relatively fast results.
When to use SEM:
SEM should be used in addition to SEO, and not alone. However, you should also use SEM for keywords or phrases that are highly competitive, and dominated by bigger names and websites. In these situations the chances that you will rank highly for it, or even get to page 1, are very low. Here, using SEM will increase your visibility. Additionally, it can be used for time sensitive products, services or information. Also to promote last minute, or short term deals and discounts.
Methods of SEO:
Keyword research:
The first step in SEO involves conducting keyword research to identify which keywords and keyphrases people are using to search for topics related to your page. This allows you to see which keywords have higher search volumes and to pinpoint the most relevant and frequently searched terms. However, it’s crucial to note that the keyword with the highest search volume may not necessarily be the best fit for your page or could be more competitive than others. Instead, focus on keyphrases that you have a better chance of ranking for, or those whose search intent aligns more closely with your content.
The key takeaway is that your page must fulfill the searcher’s query and provide them with what they are genuinely seeking. If it fails to do so, the searcher is likely to return to the search results, which sends a negative signal to the search engine indicating dissatisfaction with your result. This can lead to a drop in your page’s ranking.
On the other hand, if your page is relevant and the searcher spends time engaging with your content, or even explores additional pages on your site, this behavior sends a positive signal to the search engine, potentially improving your ranking.
On-Page Optimization:
This involves enhancing individual web pages to make them more relevant to specific keyword searches and topics. On-page elements like meta tags, headings, content, and internal links should ideally incorporate the keyphrases that users are searching for. It’s crucial that these elements are relevant to the page’s content. For instance, this article is optimized for the search term “SEO vs SEM.” That term appears in my meta title, description, URL, H1 page title, the first paragraph, and as frequently as possible throughout the text. I’ve also included the individual terms “SEO” and “SEM” wherever appropriate. As a general guideline, the keyword to content density should fall between 0.5% and 2.5%.
You can utilize Google’s Keyword tool to gather information on monthly keyword search volumes.
Additionally, Diib offers an excellent keyword explorer tool.
It’s essential to remember that these words and phrases should seamlessly fit into the natural flow of the article and on-page content. No matter how much you optimize a page for keywords, the text must remain readable and natural; otherwise, readers may be discouraged and leave your site, which sends a negative signal to search engines. It’s preferable to use those words or phrases fewer times in a more organic manner than to overuse them in a forced way. The latter practice, known as keyword stuffing, is an outdated blackhat SEO technique that modern search engines rightly disapprove of and can lead to your site being downgraded or even banned.
Off-Page Optimization:
Off-page optimization primarily revolves around acquiring backlinks from relevant and authoritative websites. The quantity and quality of inbound links signal to search engines the credibility and relevance of a website, thereby influencing its ranking. Additionally, internal linking from within your own website helps to tell a search engine how important a page is; the more internal links pointing to a page, the higher the importance of that page.
Internal linking is easy, as you have control. Although, just like with the keywording strategy, make sure you link from relevant pages within your site and when setting deeplinks from words within an article, make sure it’s relevant and clear to the reader to what and where the link will lead.
External backlinks are much more difficult, as it’s not up to you but the owner of the website linking to you. Ideally you want to get relevant backlinks from websites or businesses similar to yours, or where linking to you would be beneficial to that website’s visitors. Additionally, you want to get backlinks from websites with a high DA (Domain Authority). You can check a website’s DA by using this great free tool at Moz.
The best way to get other sites to link to you is to create good content that people want to share with their visitors. Another is to write guest articles or blogs for other relevant websites where they will allow you to place a link back to your website or article.
Technical Optimization:
Technical SEO ensures that a website is easily accessible to search engine crawlers and is structured in a way that enhances user experience. Elements such as sitemaps, good site speed, mobile-friendliness, and schema markup fall under this category.
Methods of SEM:
Keyword Research:
SEM also begins with identifying relevant keywords that potential customers are likely to use when searching for products or services. These keywords are then bid upon in auctions conducted by search engines like Google Ads. Again, it’s important to note that the keywords you bid for must be relevant to your page. Winning the bid is not only about how high you bid, but also how relevant your page is. If one advertiser bids higher than you, but your page is more relevant, then you will win the bid and your ad will be shown. It’s important that your on-page SEO aligns here with the ad keywords you are bidding for, as this is how ad relevance is determined.
Ad Creation:
Like with any adverts, you will need to create compelling ad copy that entices users to click on the ad. Advertisers can customize various elements of their ads, including headlines, descriptions, and extensions, to maximize their effectiveness.
Bid Management:
SEM requires ongoing monitoring and optimization of bids to ensure that advertisers are getting the most value from their budget. Adjustments may be made based on factors such as keyword performance, competition, and ad placement. It offers instant visibility and can generate immediate traffic to a website. However, it requires a continuous investment of resources, as traffic stops once advertising budgets are exhausted.
When to use SEO or SEM
In essence, both are two distinct yet complementary strategies for enhancing search engine visibility and driving traffic to websites. While SEO focuses on organic methods to improve rankings over time, SEM leverages paid advertising to achieve immediate results. Both approaches have their merits and can be integrated into a comprehensive digital marketing strategy to maximize effectiveness and reach the desired audience.
In fact, I would recommend using SEM in the early stages of publishing an important page or trying to sell a product or service to start building traffic to your website. Additionally, if your page contains content that is highly competitive and will be hard to rank for organically, for example selling products and competing against the likes of Amazon, then using SEM alongside SEO would be much more beneficial. If your content is not highly competitive and very niche, you might find that your organic ranking will be high very quickly.
Blogging for SEO
Blogging is a great marketing tool, so if you are blogging about a specific topic then try to search out keywords that are not so competitive and yield fewer results, especially from the higher ranking sites out there. Try to find what questions people are asking, or what problems they are trying to solve where there are little to no blogs or videos offering this solution.
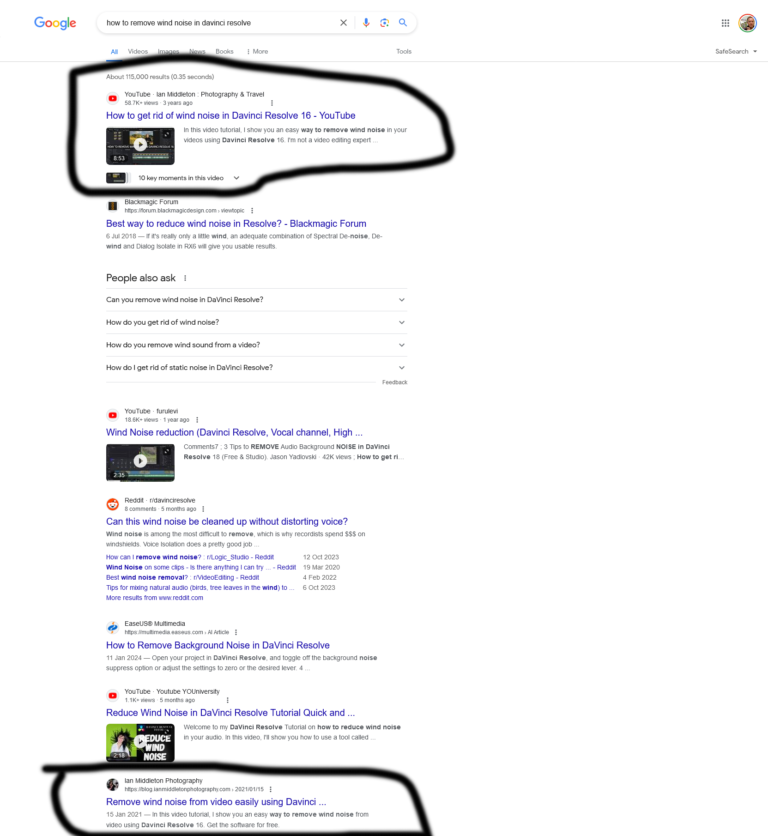
As an example, I was searching for ages to find a way to remove wind noise in videos using Davinci Resolve. When I figured it out, I made a YouTube video showing people how I did it, and turned it into a blog. My video comes up top in Google for this search and the article 6th place for the search term “how to remove wind noise in davinci resolve”
This video is among the most viewed on my YouTube channel.